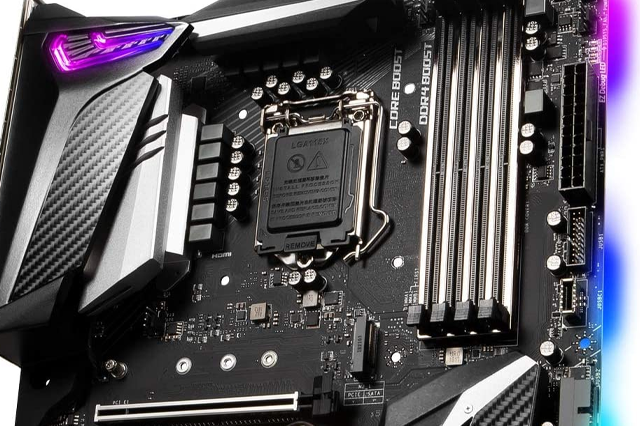
The motherboard, also known as the motherboard or main board, is one of the fundamental hardware elements for the operation of a computer. That is why it is a concept that you have surely heard if you are aware of the world of computing. However, whether you have already heard it or not, we are going to explain what a motherboard is and what it are for. This way you can solve all your doubts.

What is a baseboard
The motherboard is the most important part of a computer, a component of vital importance for its operation. The architecture of the rest of the equipment will depend on it in terms of its different internal components. That is why it is so important to carefully study the model to choose before making a purchase.
Each plate is designed to be able to place certain components on it, marking certain capacities and speed. The vast majority of the components of a computer are connected to the motherboard. It is also responsible for establishing communication between the processor (CPU), the RAM memory or the graphics card, and the peripherals that may be installed, such as the keyboard, the screen or the mouse, among others.
Four fundamental components must be installed on all motherboards for the operation of a computer, these being the following:
- The power supply.
- The RAM memory
- The processor (CPU)
- Storage units (hard drives, SSD…)
How a motherboard works
The operation of a motherboard is complex, mainly because there are numerous components installed on it. However, we must start from the basis that there are different main elements that are part of the boot process of a computer and that must be supported by the board itself to be able to carry it out.
First of all, what the motherboard does, before starting to load the operating system installed on the hard drive, is to boot the different components connected to it. The program that is located in the BIOS is in charge of analyzing all these components to detect any possible failure or breakdown. In the event that it finds it, it will emit an acoustic signal, in addition to a message that could be seen on the screen, in the event that it is started correctly.
Once the BIOS have checked the components, the internal bus that the motherboard has receives the information from the storage units, that is, from the hard drives. When it receives it, it is in charge of the connection of the processor with the RAM memory.
After this process, the data that refers to the operating system will already be duly loaded in memory and the equipment can be started. At the same time, this same main board will send signals to the graphics card, whether it is integrated into the motherboard itself or an external component.
From that moment on, with the computer booted up, it will be in charge of carrying out the exchange of data that will be managed through the different elements that are duly connected to the processor and the bus of this component.
Motherboard types
The motherboard can be presented in different formats. This way you can adapt the one that is most appropriate for the type of PC case you have chosen.
Depending on its characteristics and size, you can find the following options:
E-ATX
This is the largest format of motherboard that can be found on the market today. It has dimensions of 305 x 330 mm. They usually have different slots to be able to place expansion cards, in addition to offering greater comfort and functionality when installing graphics cards and a number of RAM memory slots that can reach 8.
ATX
Since 1995, ATX boards have been on sale, being the most common and the easiest to find. The general dimensions are 305 x 244 mm, although it is true that some manufacturers and some models have slightly modified them. However, the holes for its placement in the PC boxes are in the same place, so that they comply with the standards set to facilitate their installation.
These types of plates are commonly used for all types of equipment, from those who use them for work to gamers. In large part it is because they offer great versatility and many expansion options. There are usually seven expansion slots and four RAM memory slots.
MicroVAX
This type of motherboards has a size of 244 x 244 mm. This makes them have a square format and is smaller than ATX. They are mainly for use in the field of office automation, that is, in the office.
This is due to the fact that it occurs in users who do not require a great capacity for expansion in their equipment and who, in addition, can thus enjoy smaller-sized PC cases.
At most they offer five expansion slots, although the most common is that they are three. They also have space for four RAM memories. Attention must be paid to the chassis so that it is compatible with its use.
Mini ATX
This is the smallest size of motherboards that can be found for equipment in the home field. It has dimensions of 170 x 170 mm and is fixed through four holes that match those of ATX plates. Therefore, they will be compatible with the chassis for this type of card.
In this case, we are dealing with motherboards that only offer one expansion slot and two slots for RAM memory.
Other formats
In addition to the above, there are other formats such as XL-ATX. However, this type of motherboard is not very common, especially in a medium or low range, being more reserved for the high Premium.